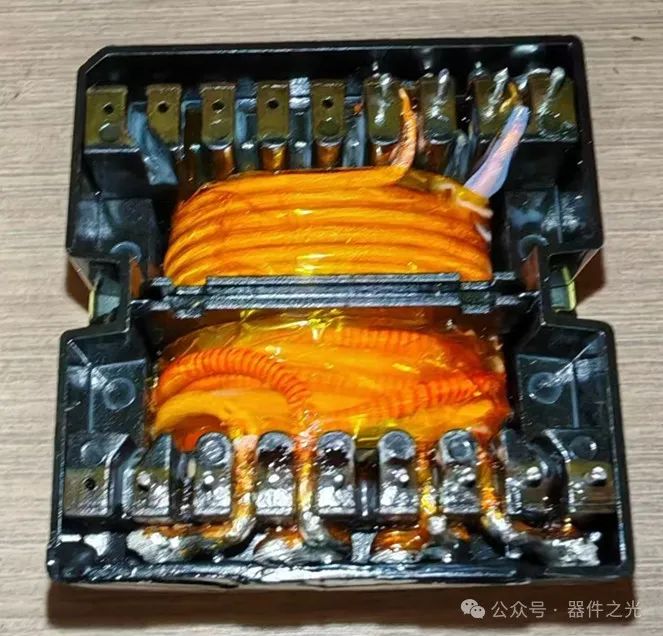
The higher the switching frequency of the transformer, the smaller its volume. So, does it mean that there is no upper limit to the switching frequency? So, can the volume be very small?
The answer is negative. In the actual working process, the frequency of high-frequency transformers is determined by multiple factors and can be divided into several aspects:
1、 Circuit topology flyback topology: Transformers have the functions of energy storage and transformation, with a commonly used operating frequency of 40-100kHz. When the frequency is below 40kHz, the volume of the iron core is too large, resulting in a larger power supply volume; When the frequency exceeds 100kHz, voltage spikes caused by leakage inductance may damage the switching transistor.
Forward topology: The common range is 60-150kHz, but it requires balancing magnetic core losses and switch losses. Push pull/half bridge/full bridge topology: Symmetrical switch driven bidirectional magnetized magnetic core, higher efficiency, supports higher frequencies ranging from hundreds of kHz to MHz, but requires more complex control design and heat dissipation.
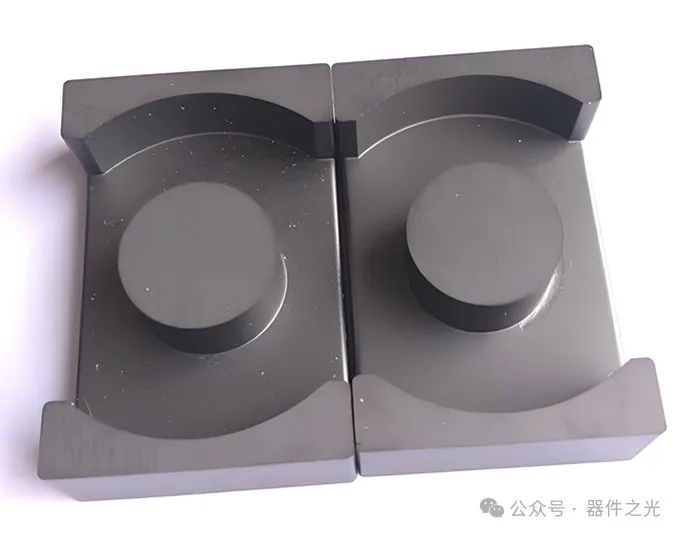
2、 The characteristics of magnetic core materials include magnetic hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. Within a certain range, the magnetic core loss increases with the increase of frequency. Therefore, different magnetic core materials should have different frequency usage ranges to ensure relatively lower magnetic core losses. For example, manganese zinc ferrite is suitable for use at frequencies ranging from 10 to 300kHz, while nickel zinc ferrite is suitable for use at frequencies above 1MHz.
Secondly, as the frequency increases, the maximum magnetic induction intensity needs to be reduced to avoid saturation of the magnetic core. For example, the magnetic induction intensity of DMR40 is 0.38T, and when designing at a frequency of 100KHz, we usually take a value of around 0.2T.
3、 Power device switching speed MOS transistor belongs to unipolar devices, with on-off time in nanoseconds. The theoretical operating frequency can reach MHz, and the actual maximum operating frequency is several hundred KHz. IGBT belongs to bipolar devices, with a relatively long turn off time and a maximum operating frequency usually between 40~50KHz.
4、 The increase in efficiency and heat dissipation frequency leads to an increase in switch and drive losses, resulting in a decrease in overall efficiency and an increase in heat generation. In order to ensure that the temperature of the product is within normal range, we need more measures to deal with heat dissipation.
5、 At high frequencies, the cost increases due to increased switch losses, requiring more measures to handle heat dissipation, leading to an increase in costs. Secondly, capacitors and inductors often experience performance degradation at high frequencies, and we need to choose devices that are suitable for higher frequencies, which increases costs. In practical design, costs are limited, which often determines the upper limit of operating frequency.
6、 Chip characteristics: PWM control chips often have frequency upper limit requirements to respond to dynamic load adjustments. This also determines that the switching frequency of the transformer is within a certain range.
Post time: Aug-06-2025